At Roche Diabetes Care we provide a holistic, therapeutic approach called integrated Personalized Diabetes Management (iPDM). Our approach strengthens the patient care process by integrating digital solutions that quickly turn data into meaningful insights. And, we do this to facilitate stronger communication and collaboration between HCP and patient for more timely treatment decisions.
Clinical studies have demonstrated improved outcomes with the use of solutions similar to RocheDiabetes Care Platform that enable iPDM.
PDM-ProValue Study Program1
Prospective, cluster-randomized, controlled interventional study program
2018
Implementing Integrated Personalized Diabetes Management (iPDM), a structured and digitally supported approach to guide the therapy process through collaborative decisions between physicians and patients with type 2 diabetes, are associated with in significant improvements in glycemic control.
Improvement in glycemic control
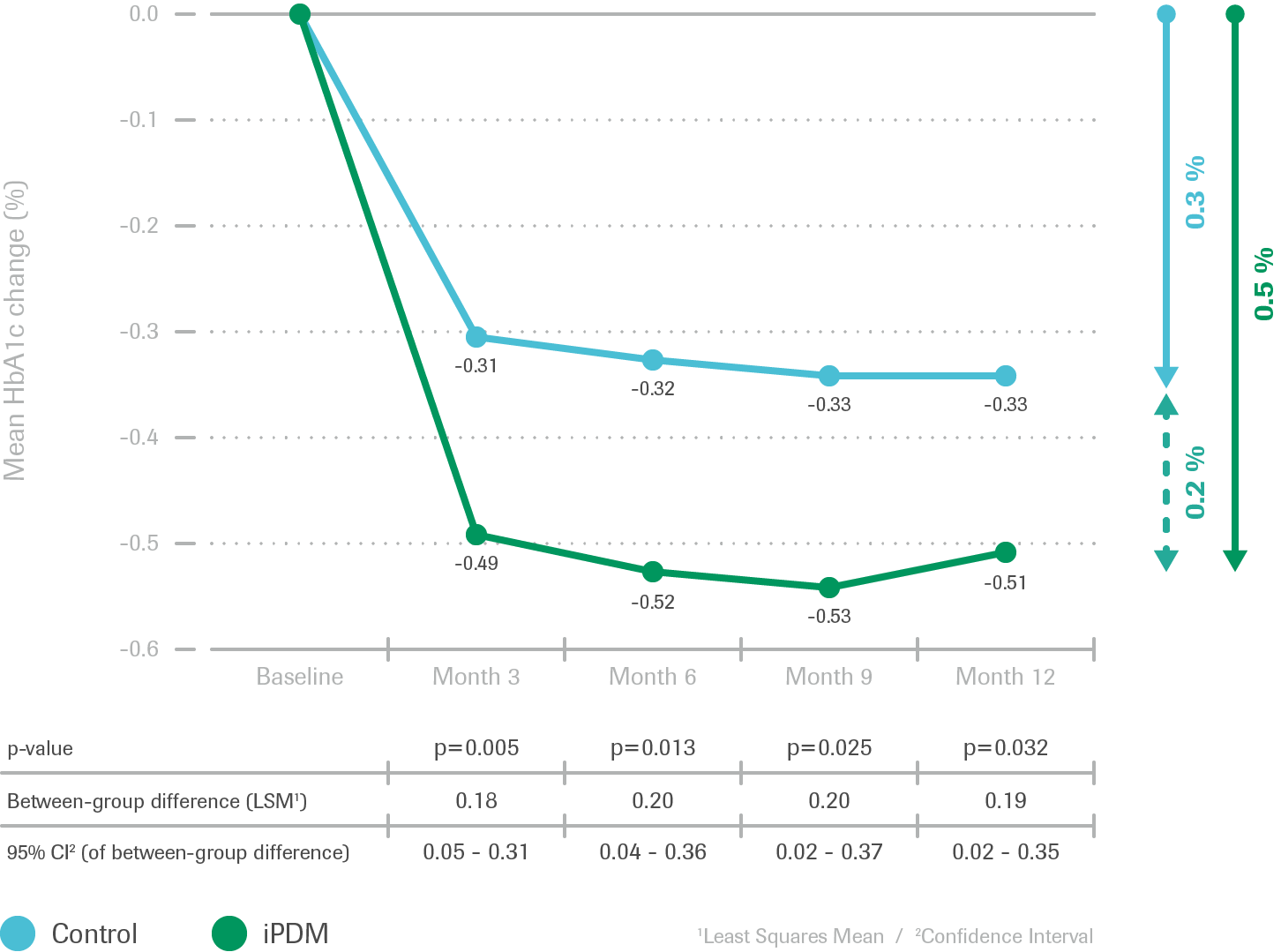
- After 12 months, improvement in glycemic control
(HbA1c reduction) was greater in the iPDM group - Rapid HbA1c reduction followed by stabilization
Earlier and more frequent insulin therapy adjustments
Recommendations for change of QAD, insulin and therapy regimen
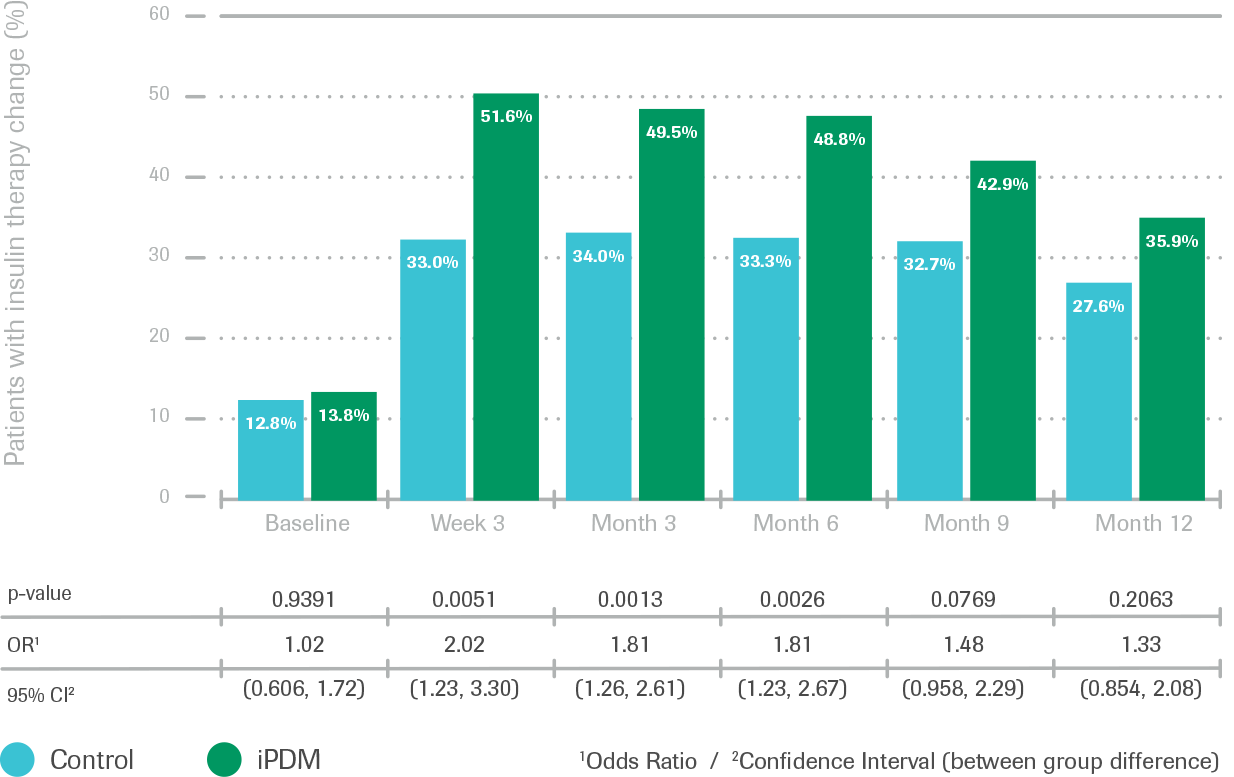
- Percentage of patients with recommended overall changes in medication (comprising oral antidiabetic medication and insulin regimen) was significantly higher in the iPDM group than the control group
Summary of results
Implementing iPDM, a structured and digitally supported approach to guide the therapy process through collaborative decisions between physicians and patients with type 2 diabetes, are associated with significant improvements in glycemic control.
PDM Connect2
Interventional single arm virtual study
2017
Use of the Accu‑Chek® Connect diabetes management system is associated with increased treatment satisfaction, reduced distress and improved glycemic control among individuals with insulin-treated diabetes.
Change in diabetes treatment satisfaction (DTSQ)
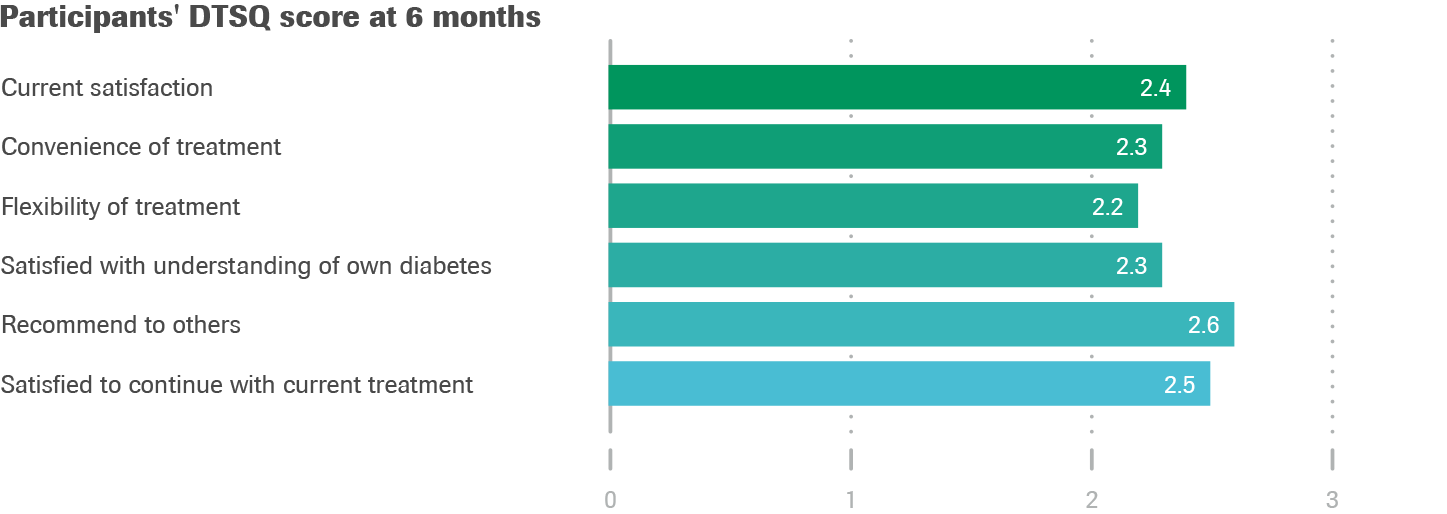
- High treatment satisfaction was seen at baseline (DTSQs):
29.8±5.8 on a scale of 0-36 (0=very dissatisfied, 36=very satisfied)
Change in diabetes-related distress
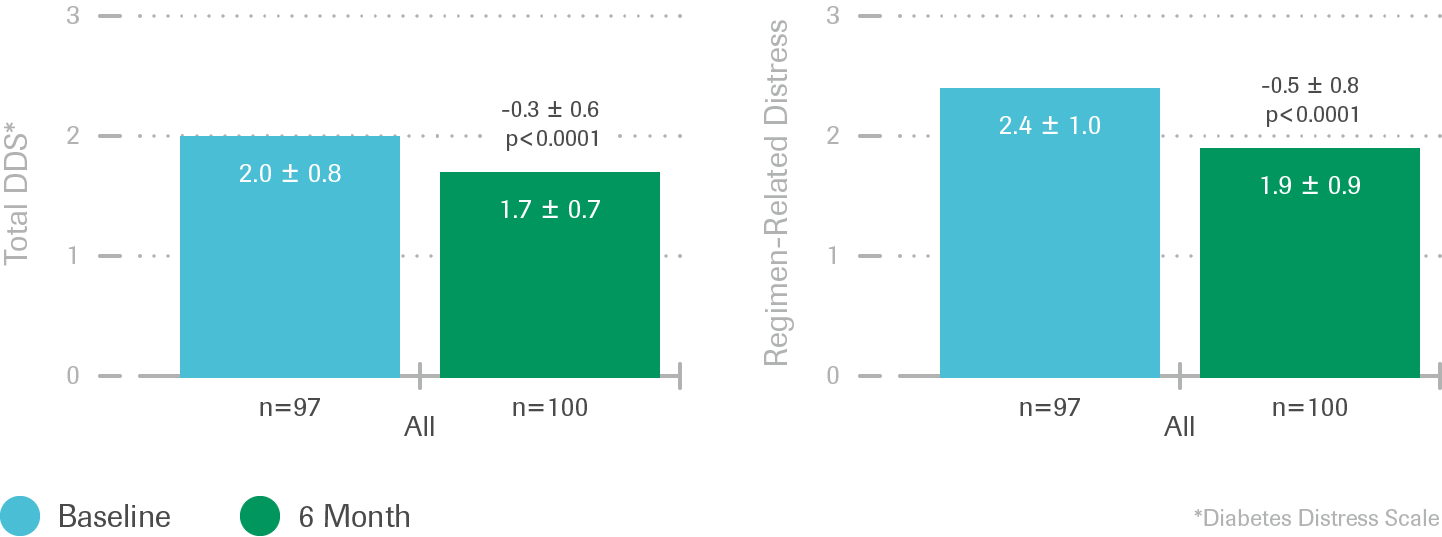
- Reductions in total mean DDS scores from baseline to 6 months were observed
Change in HbA1c: all and by practice type
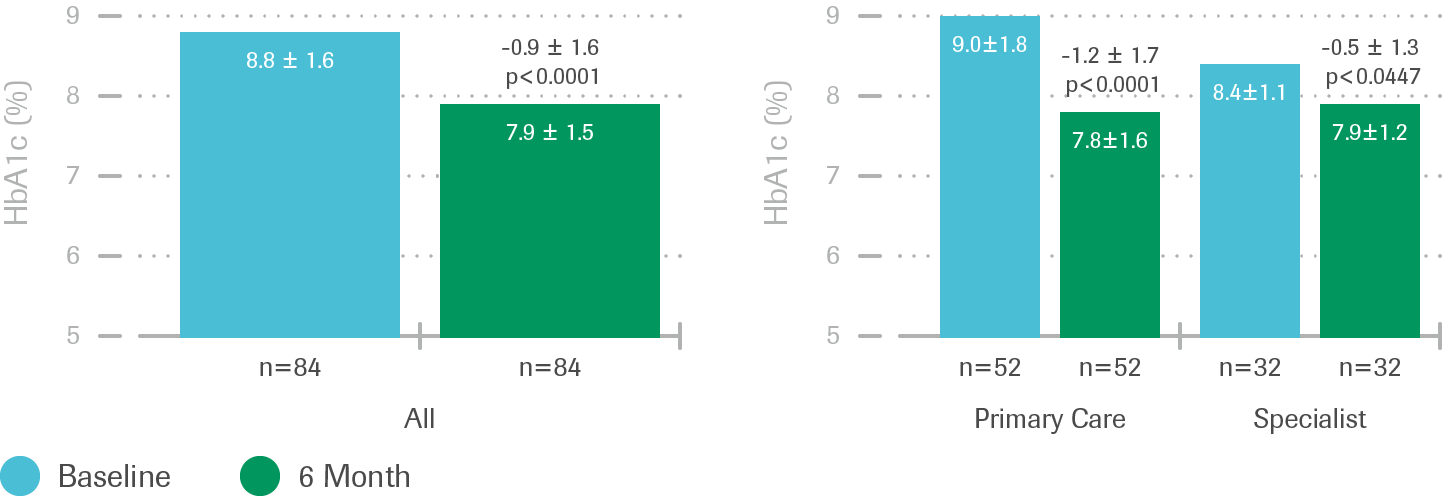
- Significant reductions in mean HbA1c levels from baseline to 6 months were observed
ACCRUES3
Prospective, comparative, virtual study
2014
Use of diabetes management software by HCPs, patients, and caregivers improves accuracy and efficiency in glucose data interpretation compared with traditional logbook data.
Improved accuracy using diabetes software
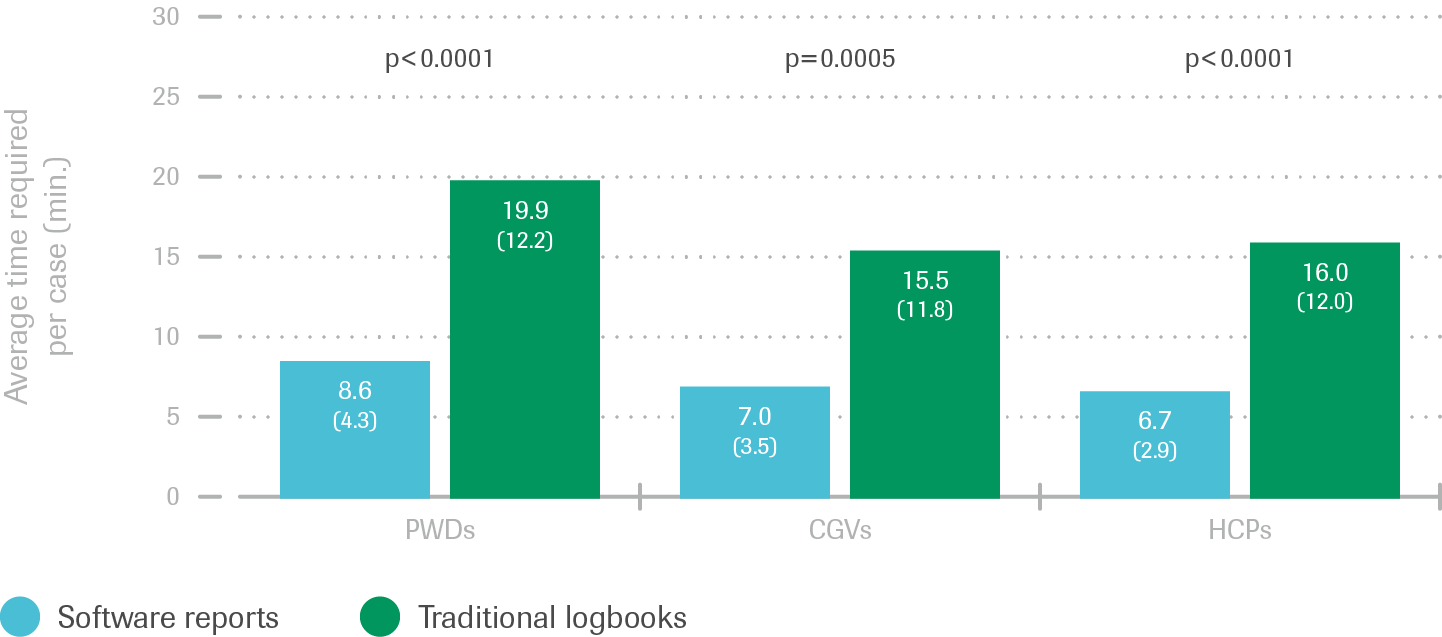
- PWD, CGV and HCP participants achieved greater accuracy using diabetes management software reports vs. logbook data
Reduced time reviewing diabetes information
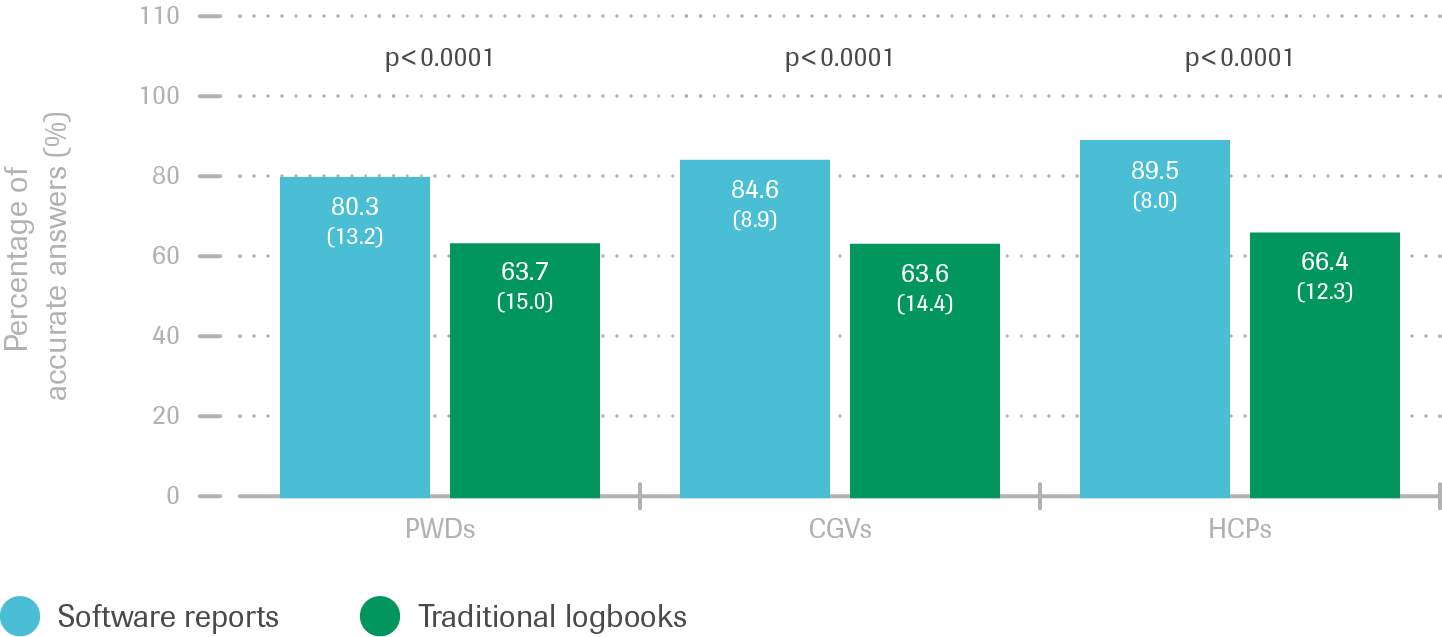
- Participants spent less time (minutes) with each case using diabetes management software reports vs. Logbook data
Summary of results
Even without prior routine use of diabetes management software, patients, caregivers and healthcare providers:
VISION4
Multicenter prospective observational study
2012
Use of pattern management with the Accu‑Chek® Smart Pix system is associated with a lower HbA1c in a primary care setting.
Improvement of medical outcome: HBA1C
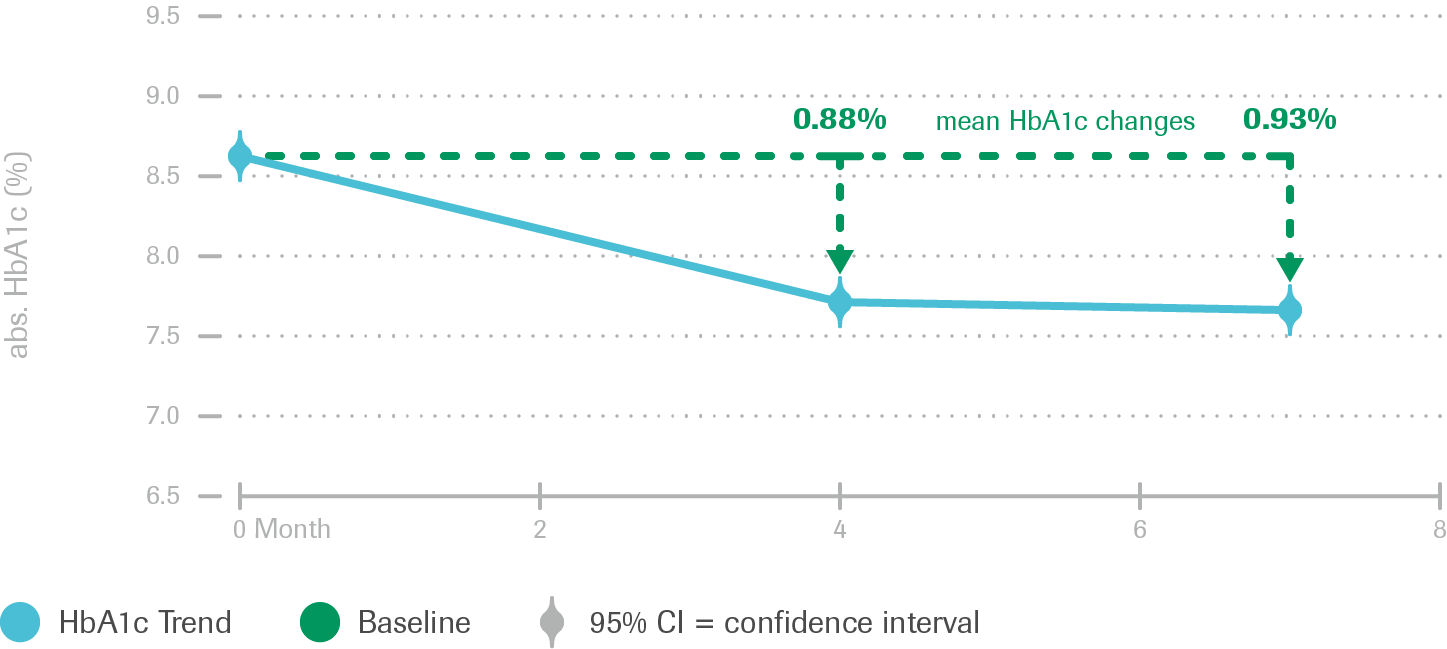
Mean HbA1c over time
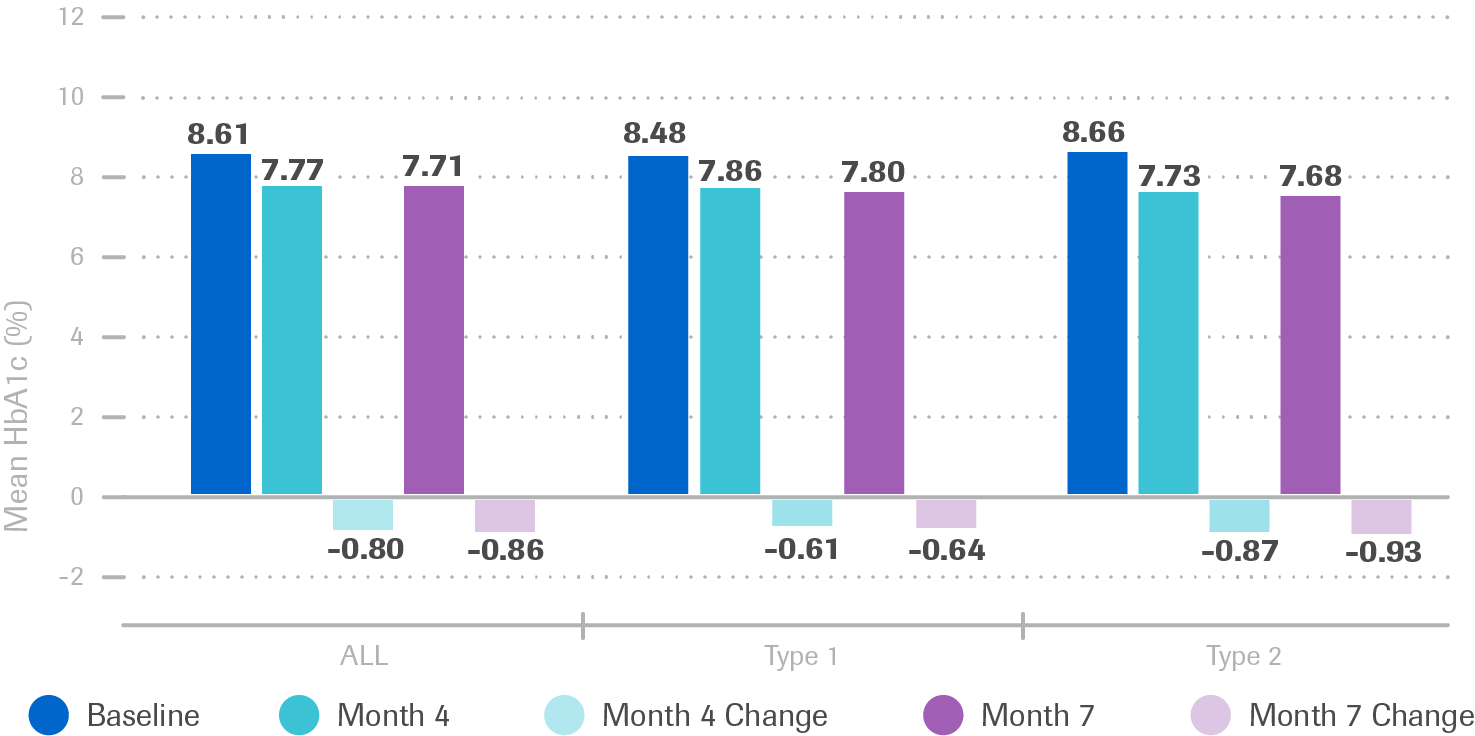
- HbA1c Trend: T1DM Patient Group (N=248)
- Significant (p<0.0001) and clinically relevant HbA1c decrease for both T1DM and T2DM patients
- HbA1c Trend: T2DM Patient Group (n=666)
- Sustained decrease in mean HbA1c for both patient groups
Improvement of process and outcome quality
According to physicians’ opinion:
Usefulness of the Accu-Chek Smart Pix system for therapy decisions (T1DM and T2DM)
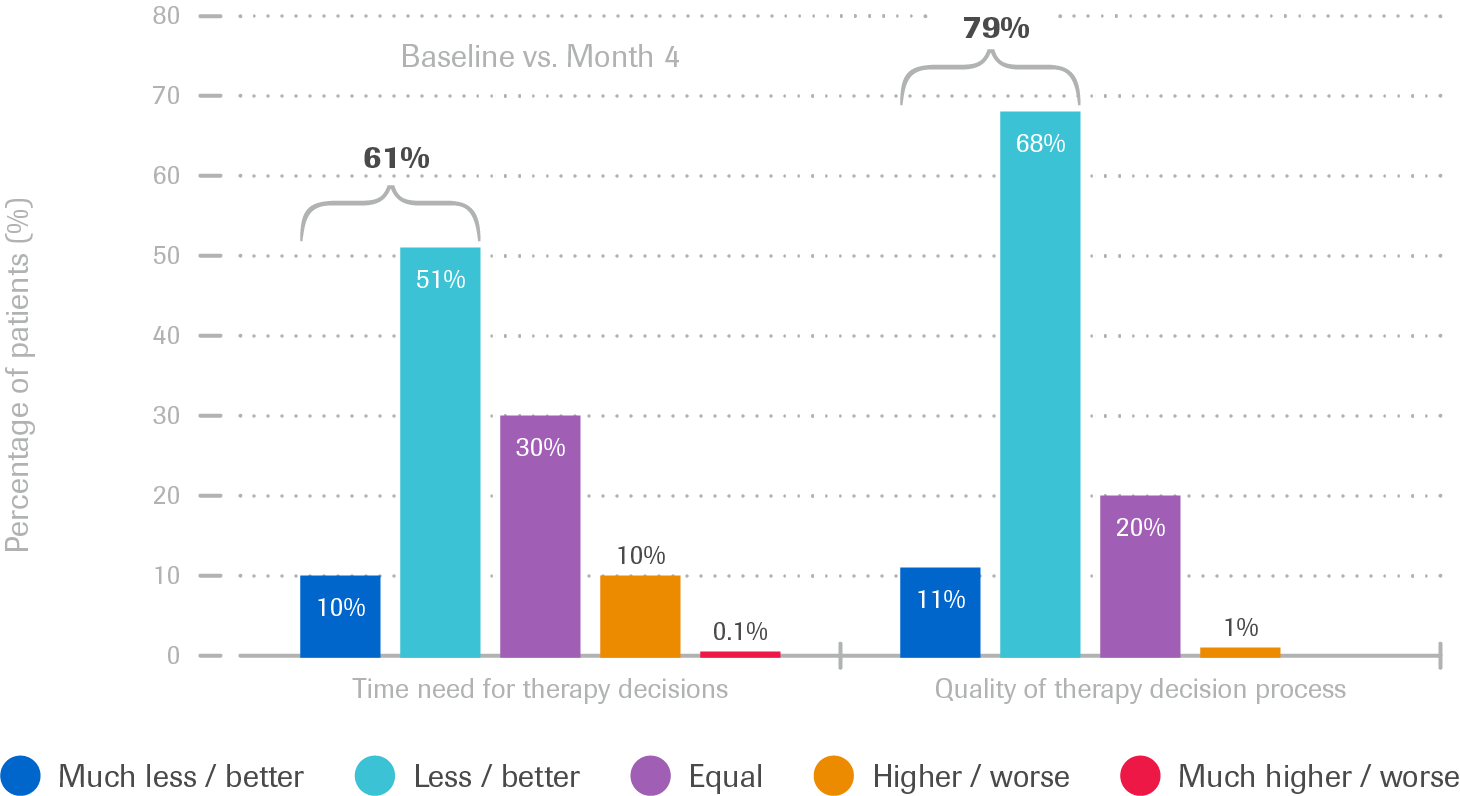
- Time need for therapy decision was reduced in ca. 61% of patient cases
- Quality of the therapy decision process was improved in ca. 79% of patient cases
Usefulness of the Accu-Chek Smart Pix system as an integral part of patient dialogue (T1DM and T2DM)
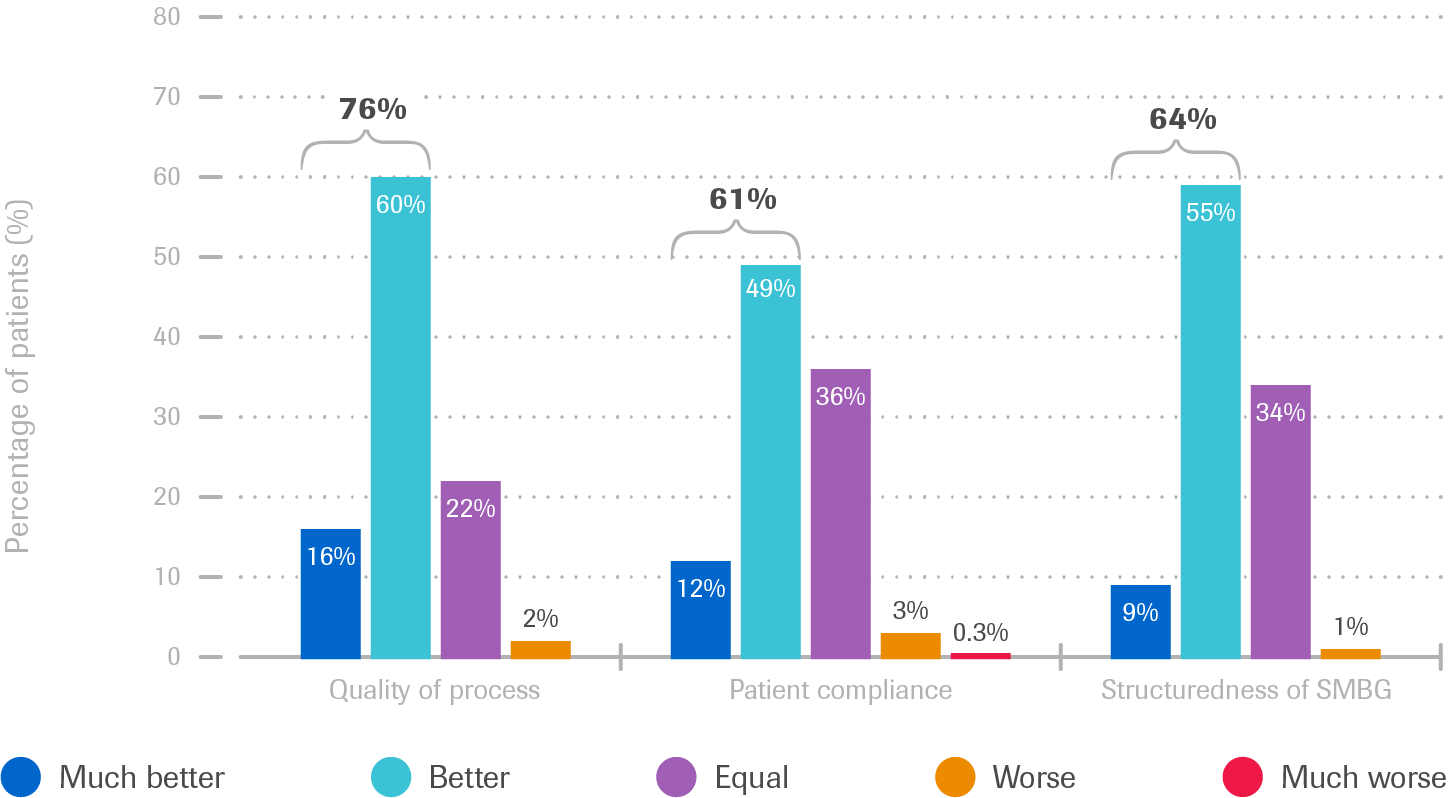
- Communication with patients was improved in ca. 76% cases
- 61% were more compliant with regard to therapy recommendations
- 64% conducted SMBG in a more structured way
Values show are rounded
*Patients assessed by physicians
Summary of results
The use of the Accu-Chek Smart Pix system was found to be a valuable part of diabetes management in “real world” practice settings within the study. It was associated with:
STeP5
12-month, cluster multicenter study
2009
Collaborative use of structured blood glucose testing supports significant improvement in patients’ glycemic control, and enables clinicians to increase frequency of treatment adjustments to support better diabetes management.
Improved glycemic control
Structured testing and the Accu‑Chek 360º View tool support reduction of HbA1c when used collaboratively with patients.
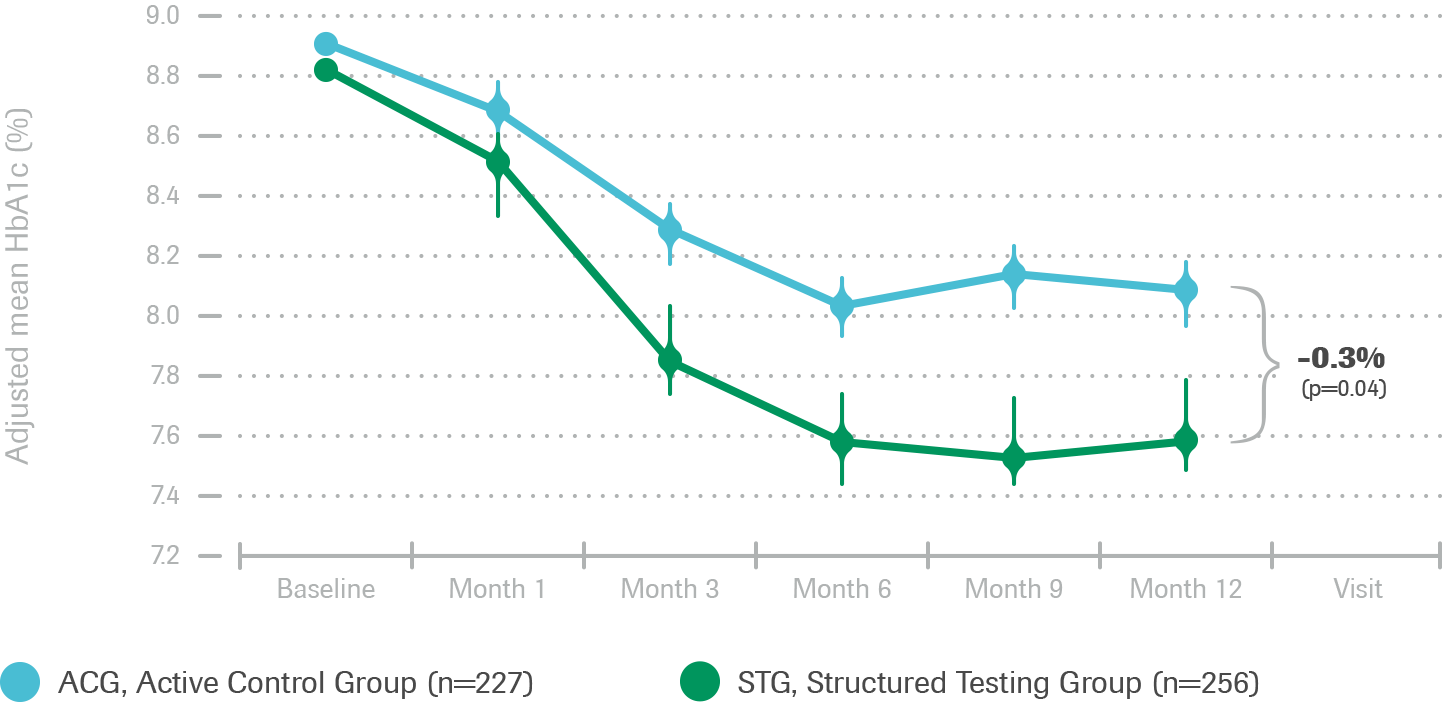
Intent-to-treat analysis: Change in mean HbA1c over 12 months
- Significantly greater HbA1c reduction over time in STG patients (n=256) compared with ACG patients (n=227)
- Structured testing intervention helped to improve HbA1c values more than the control group
Structured testing and collaborative use of the tool supported reduced postprandial excursions and better overall glycemic control.
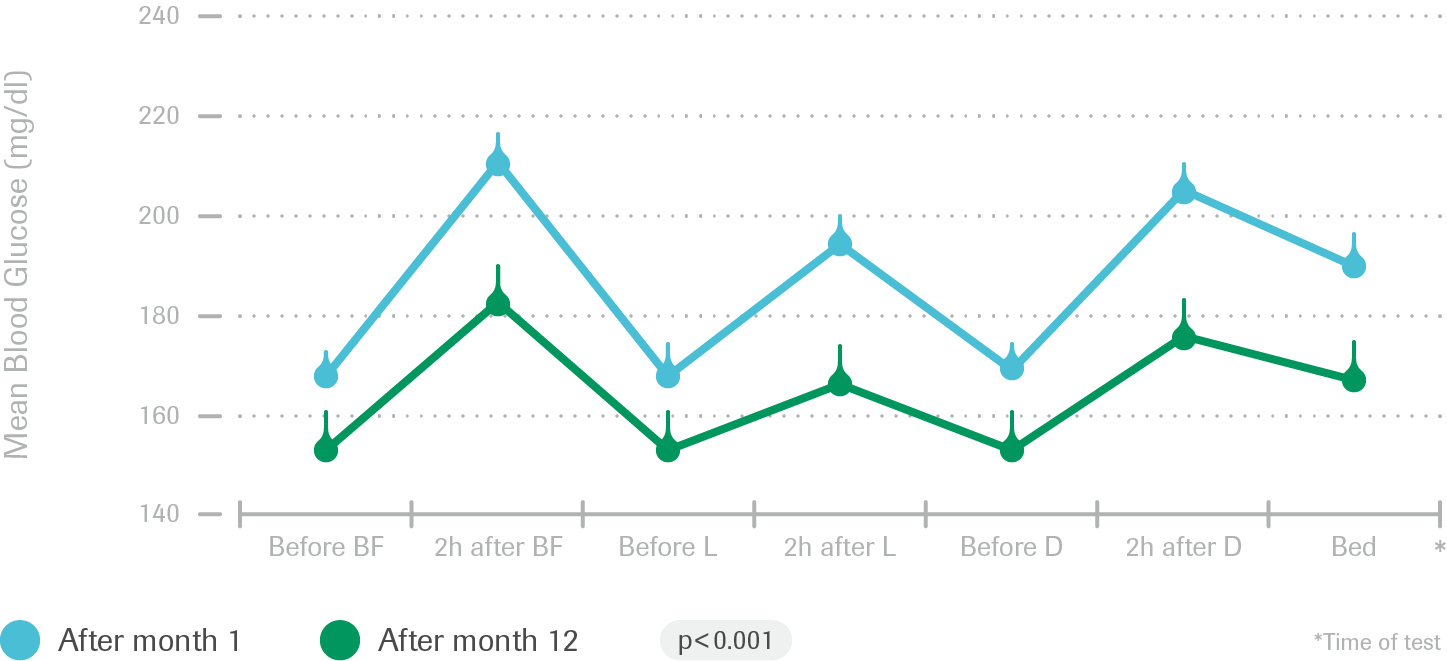
Intent-to-treat analysis: Comparison of 7-point glucose profiles at baseline and 12 months (STG)
- STG patient profiles showed lower average preprandial, postprandial and bedtime glucose levels (p<0.01) from month 1 to month 12
- STG patients significantly lowered mean postprandial glucose excursions at all meals
Therapy optimization6
Structured testing and the use of the Accu‑Chek 360º View tool enables physicians to make early and systematic therapy changes, resulting in better glycemic control.
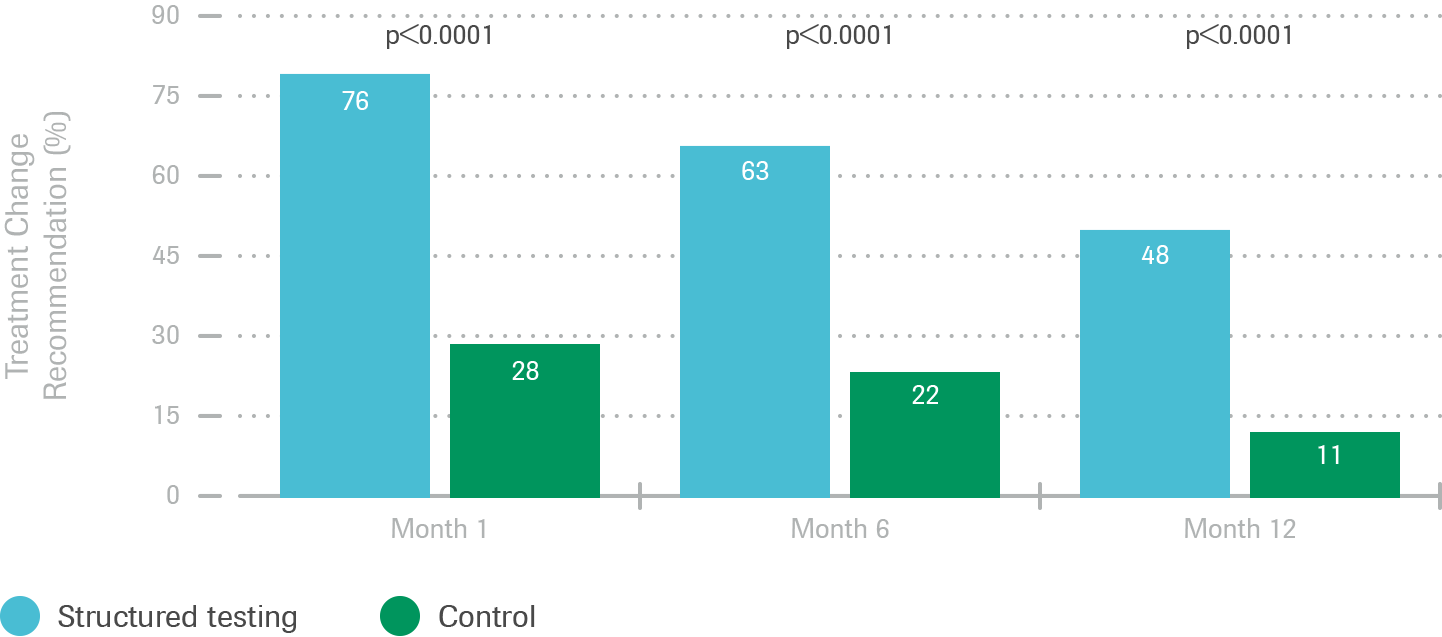
- Patients who received a treatment change recommendation, such as a drug and/or lifestyle change at the Month 1 visit experienced significantly greater reductions in HbA1c
- For the entire study, out of 5 possible visits, STG patients received therapy change recommendations at 2.7 visits, while ACG patients received therapy change recommendations at 1.1 visits